When shopping for CBD products, you're sure to encounter some industry-specific terms and may not understand exactly what they mean. Here’s a brief guide of the most common terms used to describe hemp extracts.
Crude Oil
The most unrefined form of hemp extracts. Usually extracted by using ethanol, this oil contains most of the original compounds, including cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids, lipids, and plant waxes.
Pros:
- The fullest spectrum of original compounds/active ingredients.
Cons:
- Harsh, very planty taste/after-taste
- Thick/tar-like texture and color
Distillate
Distilled oil is made by running the crude oil through an Ethanol Distiller or through a Carbon Dioxide (Co2) extraction machine. This process, shown in the diagram below, separates the various compounds that were present in the crude, yielding a more concentrated cannabinoid oil.
Pros:
- High concentration of cannabinoids (50%-90%)
- Versatile because the resulting oil does not have a strong odor/taste
Cons:
- Missing terpenes and flavonoids
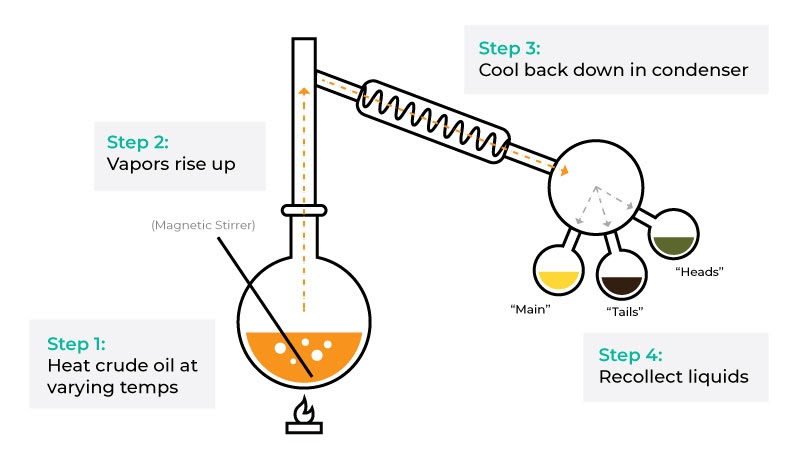
Graphic by Precision® Extraction
Full Spectrum
Full-spectrum CBD is extracted using ethanol, preserving the most cannabinoids and terpenes. Unfortunately, the name is misleading for several reasons. First, many of the active ingredients that were present in the crude oil are filtered out. Secondly, since there are hundreds of different cannabinoids and thousands of different terpenes, it is not accurate to call anything "full-spectrum". A more appropriate term for this kind of extraction is "whole-plant hemp extract" which indicates that the maximum amount of the original cannabinoids and terpenes were preserved.
Pros:
- Preserves the most of cannabinoids & terpenes.
- Least harsh taste
Cons:
- Missing most of the flavonoids and some of the terpenes that were present in the crude oil
Broad Spectrum
Similar extraction process as the "full-spectrum" referenced above, with an additional process to remove THC.
Pros:
- Similar to full-spectrum, minus the THC
Cons:
- There is less of a synergistic effect without the THC.
- Other cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids may be lost during the removal of THC
- More expensive than full-spectrum due to an extra process of removing THC
Isolate
The purest form of CBD, usually in concentrations in the range of 99% to 100%. To isolate CBD, the hemp plant must go through a series of processes. The remaining mass is then distilled using the supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) method which separates various components from the plant, in this case, specifically isolating the CBD molecule in a crystallized form. CBD crystals are then crushed into powdered form, which is then can be added to a wide range of consumer products. Given that all original elements of the plant’s smell and taste are removed during the extraction process, CBD isolate has the highest level of versatility.
Pros:
- Most versatile
- Zero THC (no high/passes drug tests)
- No taste/smell
Cons:
- Least effective, no synergistic benefits
Since the aforementioned methods utilize solvent extraction processes, we encourage that consumers review the residual solvent lab reports to ensure that any compounds that were used during the extraction have been removed from the finished product.

